Diagnostic Services

Cytologie
Cytology is the study of cells. The cellular material for testing is obtained through fine needle aspirations and pap smears. Every year, many pap smears used for screening cervical cancer are tested by Pathology-DNA and evaluated for abnormalities. In addition, thousands of tests of cellular material are conducted every year for specialists and general practitioners in the three regions. See cytological testing.
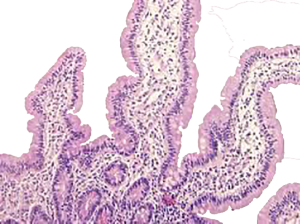
Histology
Histology or the study of biological tissues is the study of the anatomy and special functions (specialities) of tissues, i.e. groups of cells that serve the same function or form an organ together.
Submitted materials come from hospitals, private treatment centres (clinics), and general practitioners. The materials vary from small tissue samples (biopsy samples) to entire organs.
In histological testing, a section (slice) of the tissue or organ to be tested is prepared. On average, the entire process from arrival in the laboratory to evaluation of the slide and providing a result takes three working days. If additional techniques are required, the process may take longer.

Immunlogy/Immunohistochemistry
With the aid of immunological techniques, such as immunohistochemistry, an accurate diagnosis can be made. Immunohistochemistry is a laboratory technique that examines the antibodies in tumour tissue, for instance.
Using a microscope, the pathologists test whether certain proteins are present on cells. This is important information for determining the type of tumour. For some tumours such proteins are present on the cells, but not in others. Based on this, the right treatment is determined.
More information.
Molecular Pathology
Within Pathology-DNA, Molecular Pathology is an important addition to regular clinical Pathology. Molecular diagnostics are used to trace the origin of diseases. In this process, the most common genetic abnormalities in tumours can be determined.
Autopsy Pathology
An autopsy is the examining of a deceased person, baby, or a foetus that has died in the womb. Within Pathology-DNA, autopsies are performed at the request of general practitioners or specialists – who have been given permission by the next of kin – with the goal to identify diseases and find or confirm medical causes thereof. See autopsy pathology.
