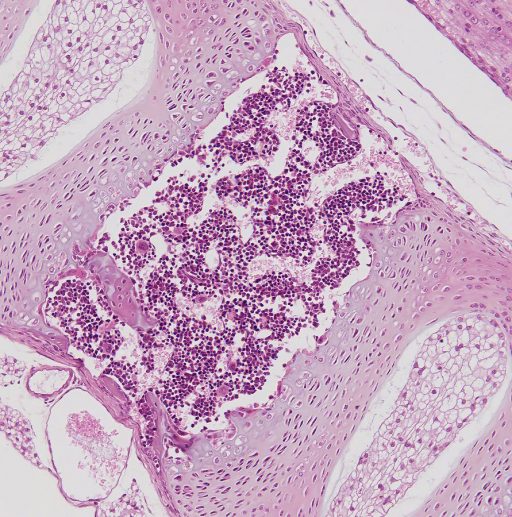
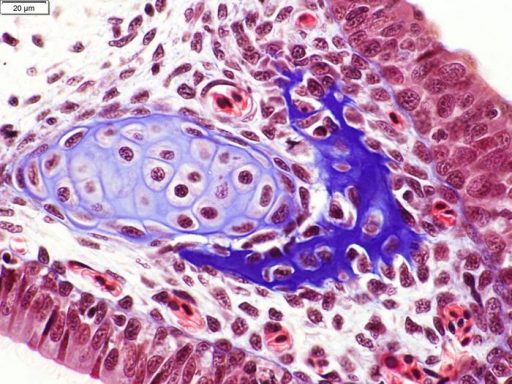
Histological testing
In order to be able to answer the clinical question in detail, histological testing is conducted. Every year about 139,000 histological tests are conducted within Pathology-DNA.
Histology or the study of biological tissues is the study of the anatomy and special functions (specialities) of tissues, i.e. groups of cells that serve the same function or form an organ together. Submitted materials come from hospitals, private treatment centres (clinics), and general practitioners. The dimensions of the material vary from small tissue samples (biopsies) to entire organs.
Liver Pathology is an important speciality within Pathology-DNA. There are four pathologists who have Liver Pathology as their focus area. This guarantees that Pathology-DNA can continuously offer high-quality diagnostics. They also consult with specialists in the Radboudumc. Part of this involves the sharing of digitised images of liver biopsies.
Approach
Received materials are first inspected with the naked eye (macroscopy) and described (size and number of tissue fragments, visual abnormalities, colour, etc. In the case of larger tissue fragments, relevant samples are taken and enclosed in a cassette. After this, it is processed and packaged in blocks of paraffin wax. These blocks are cut into slices of 4 µm, four thousandths of a millimetre. These slices are applied to slides and then stained. After this the slides are examined by the pathologist under a microscope. They look for cells showing abnormalities compared to the normal cell structure. The findings are recorded in a diagnosis that sometimes also includes a treatment recommendation. These test results are sent electronically or by post to the requesting clinician. Based on the diagnosis, the requesting clinician can determine the right treatment. The total process takes several working days.
In addition to this standard staining, special staining may be conducted to make different cell or tissue structures visible. There are also many immunohistochemical stains to demonstrate specific cell components.
Rapid Diagnostic testing
In addition to routine diagnostics, we also perform rapid diagnostic testing (frozen section procedure). This is done during surgical procedures when the surgeon wants to know during the surgery whether an abnormality is benign, or if an abnormality has been completely removed. The patient will remain anaesthetised during this examination. After learning the result, the surgeon may choose to continue the surgery or end the procedure.
1-day diagnostics for mammography abnormalities
Arrangements have been made with requesting clinicians to provide a preliminary result within one day in the case of suspected breast cancer. Because all tissue has to be sufficiently fixed in formalin, the biopsies have to be taken before 11 AM. The entire process described above will be conducted in an accelerated way, providing a preliminary result about five and a half hours later.
Examples of how tissue sections look under a microscope